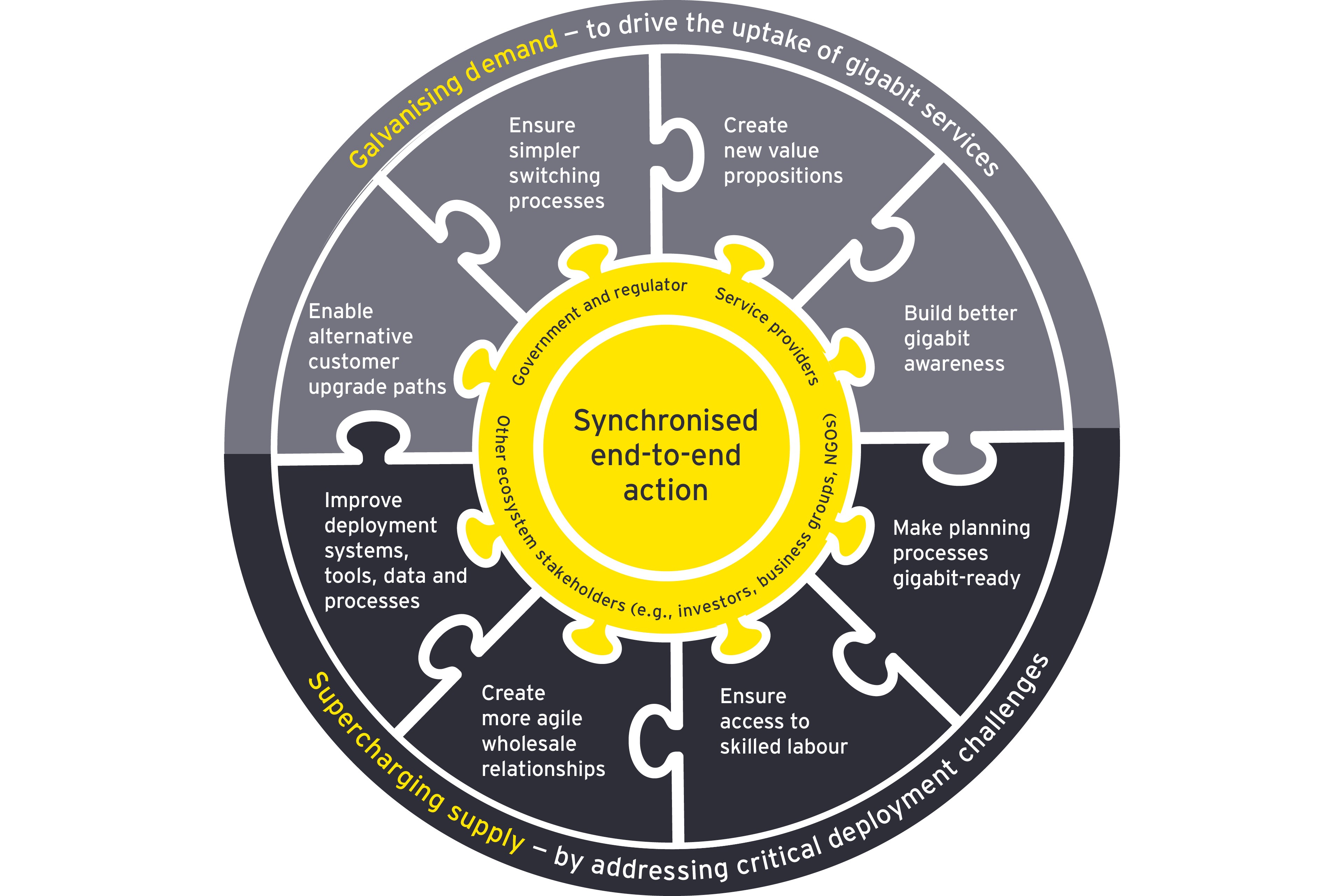
What does good look like?
When it comes to galvanizing demand, the Government, regulators and operators should act in unison to empower customers. This means combating customer apathy and inertia by demystifying what gigabit broadband can do and by making the switching process as painless as possible.
Supercharging supply will require the Government, regulators and service providers to take collaborative action across all areas of the telco value chain to ensure a sustainable and efficient gigabit-capable deployment and meet the ambitions of ‘Gigabit Britain’.
There are practical challenges to address in terms of the speed of decision-making and shared quality of information. Yet ultimately a shift in mindset is essential. The importance of bridging the digital divide should be top of mind for all industry actors. By appreciating the transformational promise of new infrastructure, all entities can work together better to create positive outcomes.
Over the coming months and years, supporting the UK’s ambition to close the digital divide and ‘build back better’ from the COVID-19 pandemic will be one of the most critical tasks facing the Government and businesses. Gigabit connectivity will play a leading role in this recovery.
For more information, please refer to the detailed report.