
Chapter 1
Impact of 5G on the GPS sector
Through advanced technologies, government can fulfil the promises and attain right results.
Key technology investments in the GPS sector
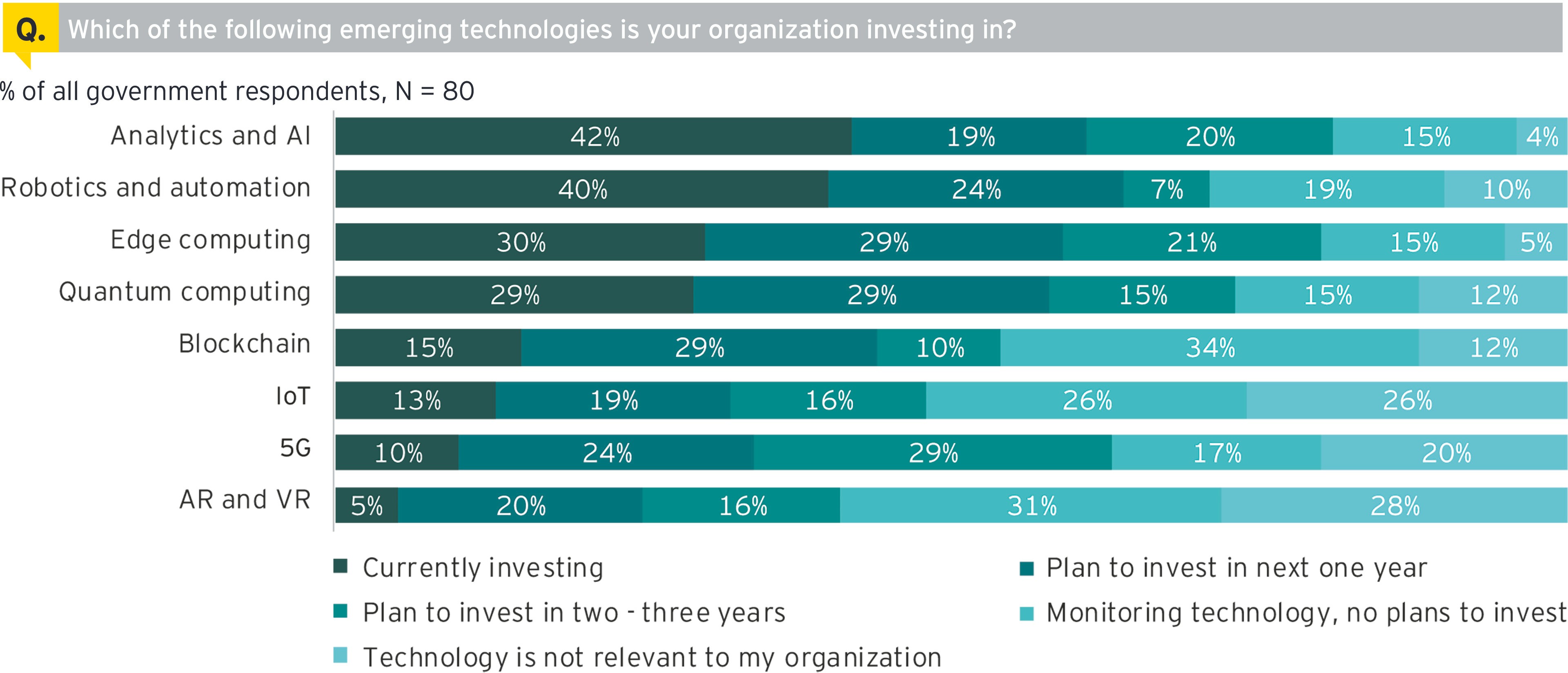
Globally, GPS organizations are investing significantly in digital technologies to realize better result orientation, operational excellence and enhance customer experience. Analytics and AI, and robotics process automation (RPA) are witnessing the maximum traction. These technologies are helping to enhance productivity, optimize processes and improve efficiency. Through predictive and prescriptive analytics, handling of big data, and AI, governments can deliver on promises and achieve desired outcomes. In addition, digital is helping governments to better understand citizen needs, wants and expectations.
Comparatively, investment in 5G and IoT is much lower. However, in the next three years, 5G is expected to witness the largest investment among new age emerging technologies for government organizations, followed closely by edge computing. Digitization of government services is already mainstream, and it has significantly improved accessibility and availability. But the full potential of digital is yet to be realized. 5G has the ability to elevate customer experience to the next level by offering an intelligent, smarter and immersive experience.
Figure : Investment in emerging technologies
Benefits and features of 5G
5G offers lightning-fast speed, i.e., 100 times faster speed than 4G, reaching maximum theoretical download speed of up to 10 Gbps. Currently, 4G latency is approximately 50 milliseconds (ms), while 5G should be able to provide 10 ms latency in general and 1 ms latency for the use cases which require extremely low latency. 5G overhauls network performance and efficiency significantly through its ability to support a thousand times more mobile data volumes and connected devices per area as compared with 4G. Most importantly, 5G opens new use cases. 5G’s primary value proposition is low latency, which enables critical communication coupled with support for massive IoT and offers significantly higher speed.
The first release of 5G commercial networks is focusing on delivering very high speed and capacity to address the ever-increasing needs of the consumer market. CSPs are using spectrum bands in the mid-frequency ranges. It allows CSPs to reuse the sites of their exiting wireless networks to easily deploy 5G. The high frequency spectrum bands are used for hotspots and fixed wireless access (FWA) deployments. Nevertheless, next releases of 5G network will progressively introduce the ultra-low latency, reliability and massive machine communications capabilities to the market.
Spectrum is a critical resource to influence 5G rollout
The standard spectrum for the rollout of 5G in three categories of frequency bands, which when combined, will allow to fully benefit of 5G network performance.
- High bands: these bands are above 20 GHz and are also called millimeter waves. Given they are very large, they allow delivery of ultra-high speed or capacity up to 20 Gbps but will provide hot spot type of coverage. They are ideal for services requiring very high density of traffic that can be found in dense urban areas.
- Mid bands: these bands range from 1 GHz up to 6 GHz and are also called centimeter waves. They will allow to deliver very high speed or capacity up to 2 Gbps and will provide reasonably good coverage in the range of up to a few kilometers. They provide a good mix between support of high bandwidth services and cost-efficient coverage of a territory.
- Low bands: these bands are below 1 GHz and will deliver high speed or capacity up to 200 Mbps but will be able to provide very good coverage up to several kilometers. These bands are ideal for massive IoT communications to support the traffic generated by many sensors, each generating low-to-mid traffic over a large territory. So, depending on the type of services that the government will want to roll out, central governments might have to start by releasing some bands vs others, or in the meantime leverage 4.9G technology which is already enabling lots of new digital services.

Chapter 2
How can 5G transform government service delivery?
Key application areas of 5G in the GPS sector — living, service and regulatory environments.
Emerging technologies such as AI, robotics, blockchain and IoT are now being used to solve real-life issues and problems. It is leading to provide better services and a living environment for citizens. The advent of 5G has simply catapulted digital service delivery to new levels. With 5G, the potential to transform the lives of citizens is immense.
Living environment
5G is expected to have a much bigger impact on the living environment, significantly enhancing the citizen experience. Currently, CSPs are using mid or high spectrum bands for deploying 5G services. It is best suited to cover city areas. Therefore, initial government services leveraging 5G will be around smart city services. Along with IoT, 5G is expected to play an integral role in smart cities. With the increase in smart city applications — both in volume and velocity — it may be difficult to manage the exponential growth in end points or sensors. 5G is expected to overcome this challenge through its ability to connect many end points or sensors as part of its massive IoT functionality. Considering the huge impetus in developing smart cities, this is likely to emerge as a key use case for government service delivery.
Early 5G use cases have focused on offering enhanced mobile broadband in densely populated urban areas, complementing 4G and other alternative networks to provide connectivity and augment capacity. Governments can partner with CSPs to offer 5G hotspot services in public places. Citizens can access ultra-high definition (UHD) videos and content at a specific spot or on the move (e.g., buses and trains).
For local government authorities, traffic management is a key focus area. Through real time dissemination of information and analysis, authorities can optimize traffic flow, control traffic lights and issue advisory to drivers. Moreover, providing real-time updates on public transport systems can help citizens to plan better and save crucial time.
Ensuring the safety of citizens is on top of the list of all local governments and law enforcement agencies. 5G can enhance real-time video surveillance significantly, by enabling higher throughput wireless alternative to fixed connections. In addition, 5G supports higher resolution videos and images, improving the quality of analysis. The transmission of a large amount of real-time data and high-quality images will go a long way to prevent and respond to crimes.
Service environment
Governments offer numerous services — passports, driving licenses, national IDs, business licenses, etc., that are directly controlled and delivered by them. These primarily fall under the purview of the service environment. In the last decade or so, increased digitization has fundamentally changed how government services are rendered. For instance, accessibility of services has increased manifold through online portals and mobile apps.
The adoption of 5G is expected to help governments offer a better service experience for citizens. The use of immersive technologies is touted to be the next big frontier of customer experience. VR, AR and MR are sensitive to network performance. 5G will offer larger capacity, lower latency, and a more uniform experience for various immersive technologies. To elevate customer interaction, if all government online forms and applications can be accessed through AR devices, then citizens can benefit from a more intuitive and visually enriching experience. Even in-department signages can be radically transformed through a combination of AR, VR and MR. The level of customer interaction and engagement will surely be enhanced.
Another area where immersive technology can play a key part is customer service. Imagine a world where citizens are interacting with government customer service agents through AR-enabled devices. The customer service representative will appear in the citizen’s space and allow for face-to-face interaction. Or simply, a government service representative resolving citizens’ queries through an HD video chat. A lot of scenarios will emerge that are futuristic. However, there is no doubt about the limitless possibilities of 5G in enhancing customer experience.
In health care, 5G has the potential to make the maximum impact on the lives of citizens. A smart ambulance equipped with the latest medical instruments, including HD video camera and portable MRI scanners, can help to transfer real-time data to the hospital. This will help to reduce the door-to-needle time and ensure emergency care within the golden hour. Even the transfer of large data files within the hospital can be much faster using 5G and multi-access edge computing (MEC) networks. 5G can open new use cases such as remote surgery, where specialist doctors can perform tele-mentored surgery in remote areas. It will enable care to be delivered virtually from anywhere and anytime. Overall, the adoption of 5G in government hospitals will help to connect various applications, people, devices, robots and processes to enable a holistic digital experience for patients.
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has put the spotlight on health care systems and infrastructure. 5G is already improving select medical activities to help in the treatment and control the pandemic. For example, 5G is enhancing the efficiency of medical personnel through remote diagnosis. The COVID-19 pandemic is transitioning health care delivery online. 5G is expected to make the online experience much better and become the backbone of key technologies such as telehealth and telemedicine. On the ground, 5G-enabled mobile trolleys are helping to minimize the number of contacts between medical staff and patients. Eventually, 5G will open several opportunities around automating health care processes. Already, 360-degree cameras connected to 5G networks are being deployed to stream data in real-time from ICUs. It will help doctors in different locations to ensure the right treatment.
Regulatory environment
The regulatory environment is facing a tectonic shift in the digital era. In a hyper-connected world, traditional regulatory boundaries are getting blurred. A siloed approach will not work for emerging digital technologies such as 5G and AI. Increasingly, sector regulators have to cooperate with other sector regulators to define a common overarching roadmap for the success of new technologies. 5G encompasses a wide range of industries and involves close coordination between different government departments. Without coordinated standards and policies, the true benefits of 5G will not see the light of day. Consensus on policy matters, common standards development and achieving end-user objectives should be the key priority for sector regulators.
South Korea’s 5G policy is the most mature and evolved, with a clear roadmap, significant investments (joint government and private), development plan for vertical industries and use cases, and pronounced tax incentives for 5G rollout. Successful implementation of the initial 5G strategy has led the Government to formulate a “5G+” plan. The Ministry of Science and ICT, and nine other related ministries jointly developed the 5G strategy. It aims to create a US$26b ecosystem for 5G-related services and industries in South Korea by 2023.
5G policies in majority of the countries focus on common parameters — making 5G spectrum available, support for 5G infrastructure rollout, fostering cooperation and dialogue between various stakeholders, and identification of new use cases. All national 5G policies focus on developing a sustainable 5G ecosystem. There is strong political commitment for 5G, and this translates to varying degrees, into institutional mechanisms and collaboration platforms with industry. Governments are making significant investments in 5G in conjunction with private enterprises.
Related article

Chapter 3
5G deployment models
The role of CSPs and private networks in 5G deployment
5G being a licensed spectrum technology, its primary deployment model will be through CSPs. Given the much more widespread usage of 5G across vertical industries, central governments might want to allocate some of the 5G spectrum for private wireless networks — supporting critical applications such as defense, public safety, utilities or railways which have very specific constraints in terms of communication reliability.
State and local governments that will need 5G services to deploy their smart city services might also have an expanded and more active role in the deployment of 5G on their territory.
On one hand, CSPs own the spectrum, but might face difficulties in deploying 5G in the highest bands, the one that offer the best speed and capacity, as:
- Given the small coverage of cells, it requires a strong densification of 5G antennas, which means having access to street assets to provide a good city coverage.
- Deployment of these antennas is costly, and they need to define proper return on investment (ROI), before investing.
On the other hand, local governments need 5G connectivity to power their smart city services and they own many street assets or city real estate.
Role of private networks in 5G deployment
5G is opening numerous new business models for key stakeholders such as governments and enterprises apart from CSPs. Leading industry conglomerates are planning to deploy captive 5G private networks to capitalize on new Industry 4.0 opportunities — automation, large number of connected devices and sensors, and usage of immersive VR and AR technologies. Setting up a private 5G network offers several benefits. Firstly, private 5G networks are expected to augment the performance and quality of corporate network connections. It is easier to deploy 5G network within an enterprise campus that has access to power and backhaul network, than at public locations. It essentially overcomes some of the limitations of Wi-Fi and wired Ethernet by offering low-latency support for real-time performance requirements for applications such as robotic motion control. A private 5G network provides greater control over security and allows sensitive and proprietary data to stay local. Overall, critical communications and industrial IoT segments are expected to drive the deployment of public 5G networks, primarily due to the need for wide-area and ubiquitous coverage requirements of nationwide public safety networks, enterprise buildings, public venues, factories and warehouses.
Related article

Chapter 4
Key considerations
Five aspects that can help governments to leverage 5G in transforming service delivery.
- Governments should consider establishing specific innovation labs to explore how the power of 5G can be leveraged to create a virtual always-on government model for the access and delivery of services.
- Governments should, other than spectrum auctions, consider nonconventional options for rolling out 5G, as this could potentially accelerate its deployment and deliver more value in the long run.
- Both CSPs and governments have complementary assets and converging interest to help deploy 5G in cities. They must choose the appropriate model to facilitate the rollout of 5G
- Governments should take a proactive approach to develop new 5G use cases that has the potential to significantly improve the quality of life and enhance citizen experiences.
- Governments and other stakeholders should actively explore partnering and collaboration options that will bring into play everyone’s strengths and enable the development of innovative and unique business models. It will facilitate and accelerate the deployment of 5G networks.
Summary
5G will transform government service delivery across the living, service and regulatory environments. It is time to adopt it with full gusto and realize its true benefits in the now, next and beyond. The discussion revolves around the 5G deployment models in the GPS sector and outlines key considerations for government organizations and CSPs to capitalize on the 5G opportunity in the GPS sector.


