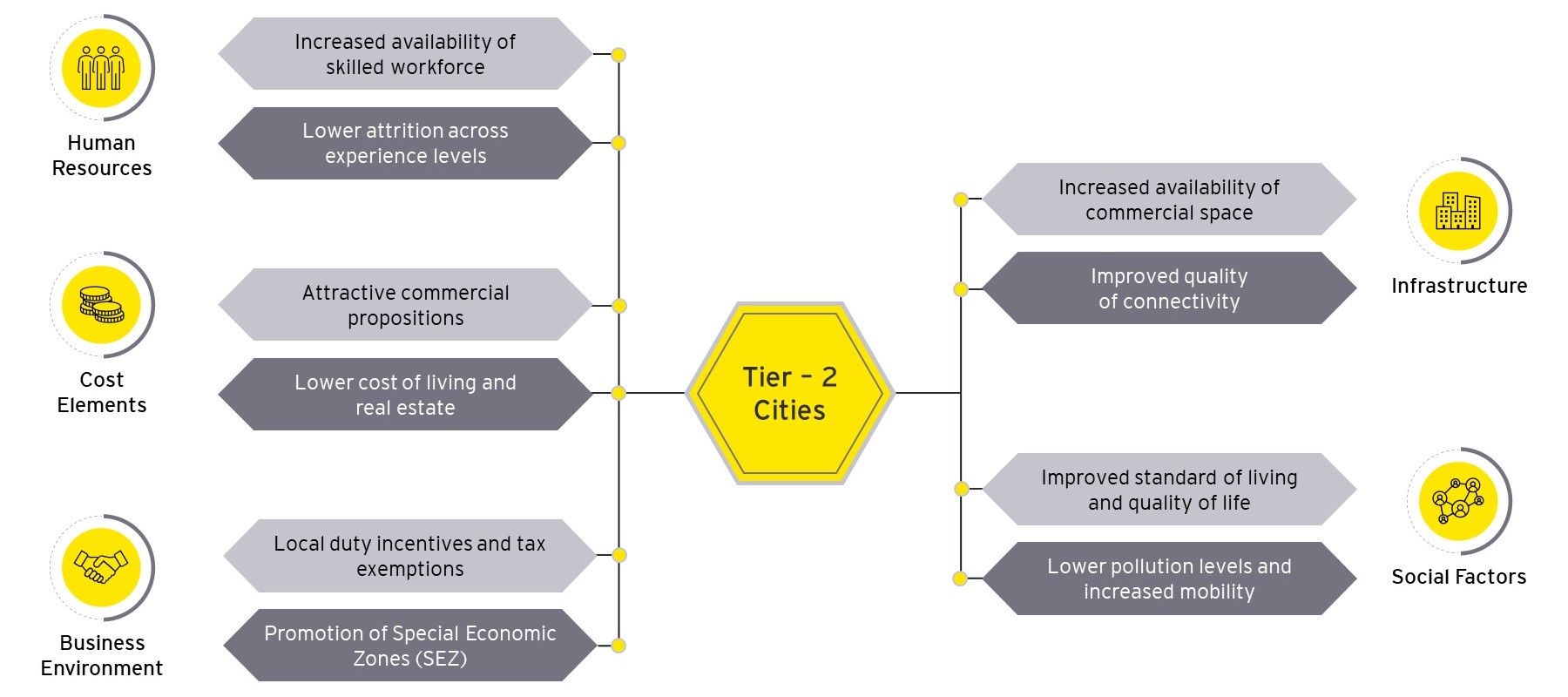
1. Human resources
Tier-2 cities have evolved with respect to the availability of skilled and employable resources. As per the India Skills Report 2023, Lucknow and Mangalore, which are Tier-2 cities, fare in the top three most employable cities in India. Tier-2 cities are becoming centers for specialized and niche skill requirements; Coimbatore, amongst others, has emerged as one of the locations for engineering services. Additionally, attrition rates in Tier-2 cities have been observed to be up to 10% lower than Tier-1 locations[3].
2. Cost elements
Lower costs of talent and infrastructure in Tier-2 cities, as compared to Tier-1 cities, are contributing to a reduction in the Total Cost of Operations (TCO). A recent analysis shows that Tier-2 cities typically have 10% - 35% lower cost of living as compared to the nearest Tier-1 location. According to a CBRE 2022 report, relatively affordable cost of living, increasing presence of healthcare facilities and educational institutions support the quality of life in Tier-2 cities as compared to Tier-1 cities.
3. Business environment
While Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to promote IT/ITeS industry have been set up in Tier-2 cities, State Governments are also incentivizing businesses that are setting up new centers or expanding existing setups into non-Tier-1 locations. For instance, as per Tamil Nadu ICT policy 2018, new or expansion of IT/ITeS industries located in B&C districts will be provided an additional capital subsidy of 10% and 25% respectively over and above the eligible limit.
4. Infrastructure:
As per the latest mobility index reports, two of the top five cities in mobility infrastructure are Tier-2 cities, namely, Bhubaneshwar and Jaipur, and some of the Tier-2 cities have better road infrastructure as compared to a few Tier-1 cities. Tier-2 cities are also witnessing an increase in scheduled domestic passenger traffic as compared to Tier-1 cities. Government of India, under the UDAN scheme, is focusing on better air connectivity to Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities and providing necessary incentives. Tier-2 cities have recently seen a high growth in coworking spaces. For instance, Chandigarh, Jaipur, Kochi, Ahmedabad, Lucknow, and Indore have more than four flex operators while Bhubaneshwar, Visakhapatnam, Thiruvananthapuram, and Coimbatore have more than one flex operator in the city.
5. Social factors
Five of the top 10 cities in the Ease of Living (EOL) index are Tier-2 cities, namely Ahmedabad, Surat, Coimbatore, Vadodara, and Indore. Lower pollution levels and better air quality index as compared to most Tier-1 cities are some of the other contributing factors to making Tier-2 cities more attractive. Subsequently, Tier-2 cities have surpassed pre-pandemic air passenger traffic numbers, which is also a sign of increased mobility in Tier-2 cities.
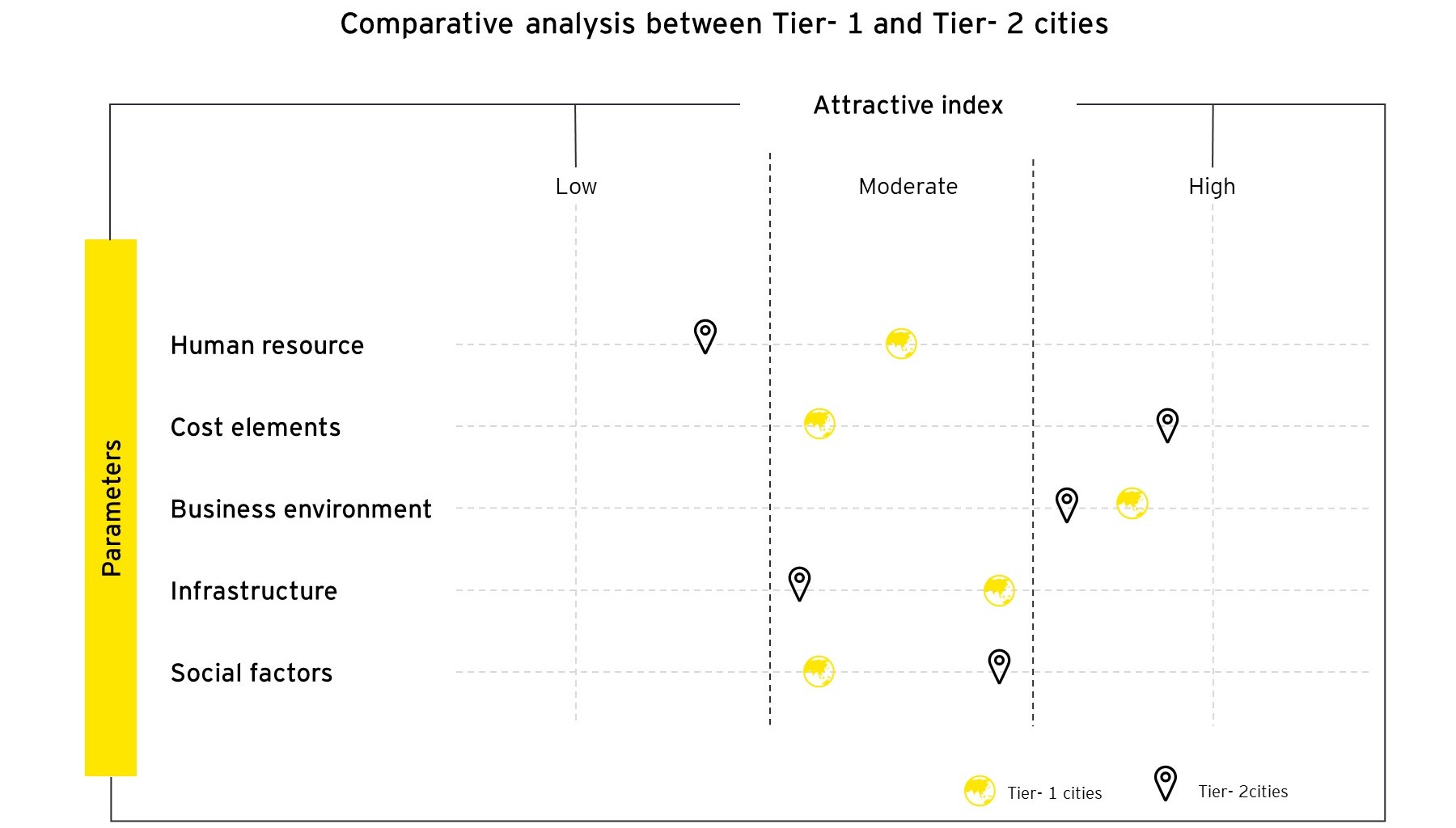
The chart below shows a comparative analysis between Tier-1 and Tier-2 cities across five parameters — human resource, cost elements, business environment, infrastructure, and social factors.