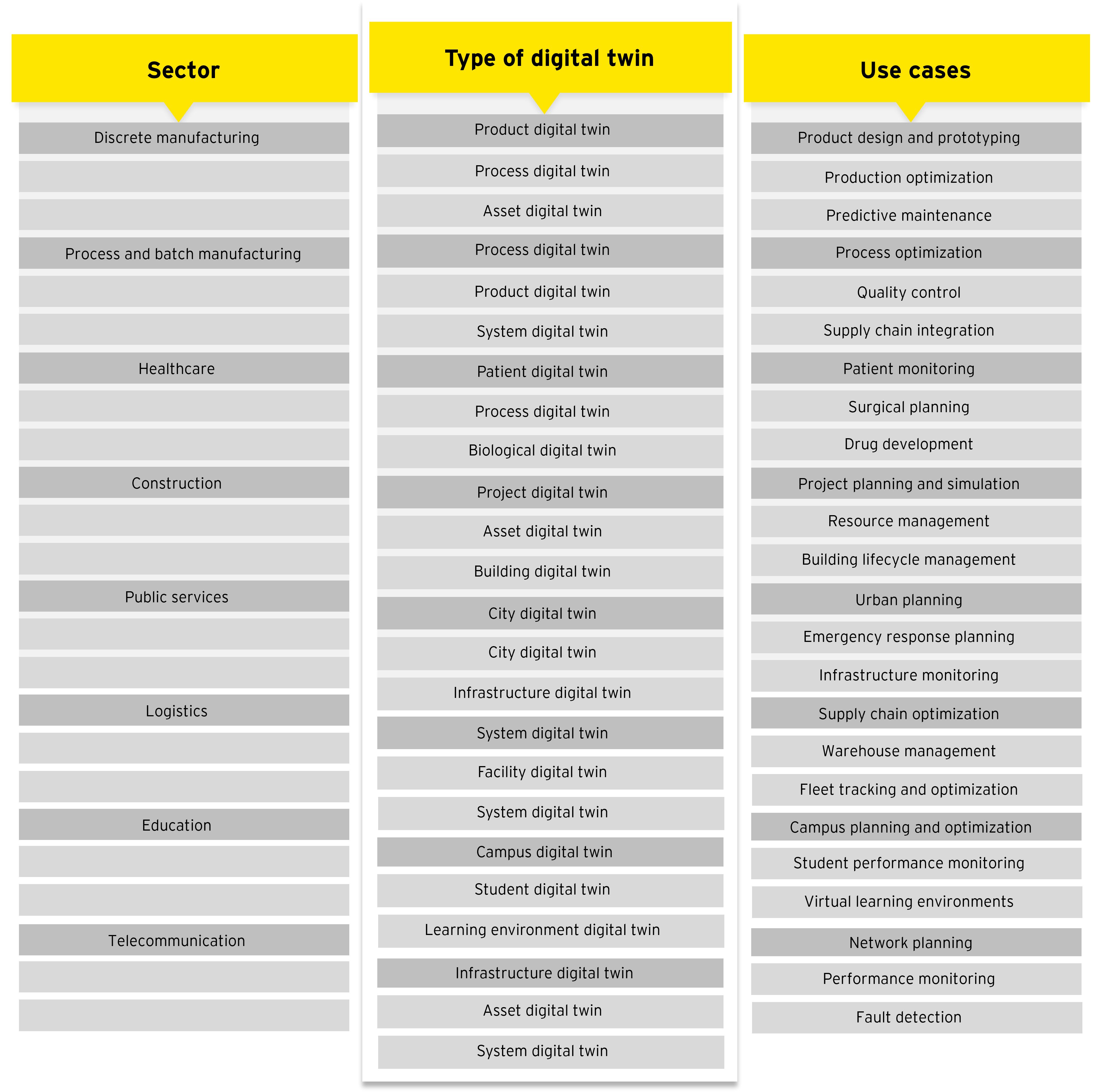
Diverse digital twin applications
Digital twins' applications vary by sector due to factors such as technology, network connectivity, skills, interoperability, data standardization, and governance. But OEMs are the biggest adopters, especially in new manufacturing operations. The automotive sector holds more than 15% of the market share of digital twin adoption, with significant demand in the electric vehicle (EV) segment. In fact, a global EV major employs component digital twins to monitor vehicle parts in real time and predict issues before they manifest. This enhances the overall lifecycle, safety, and performance of its EV cars.
Other early and heavy adopters include manufacturing, healthcare, infrastructure, smart cities, and agriculture sectors.
Manufacturing: Organizations are using virtual replicas of production lines, machinery, and factories to simulate and optimize processes, improving production planning, minimizing downtime, and reducing maintenance costs. A global aviation company is using component digital twins to predict 99.9% of anomalies in its jet engine parts, while a manufacturing company is using process digital twins to optimize various parameters, resulting in a reduction of defective products by 75%. An oil company has deployed process digital twins to optimize the drilling process on its oil rigs, resulting in reported savings of up to US$1 million per day.
Healthcare: A medical center in the US is developing digital twins of patients' kidneys to improve surgical outcomes and provide enhanced training for surgeons. Similarly, an Indian healthcare company is utilizing this technology to develop patient-specific heart models, enabling treatment simulation and evaluation without invasive procedures. Personalized treatments are now possible by creating virtual patient models for precise diagnosis and treatment planning. To improve skills and minimize errors, surgeons are using process digital twins to simulate complex procedures.
Infrastructure and smart cities: Digital twins are being utilized to simulate human behavior, including crowd dynamics in urban environments or emergency scenarios, addressing critical political and societal decision-making needs. The Survey of India is actively creating digital twins of major cities that accurately mirror the urban landscapes and physical assets. These detailed models not only aid in city planning and policymaking, but also enhance disaster management efforts. Recently, the Indian government launched Sangam, an initiative focused on digital twins for future infrastructure planning and design, leveraging innovative integration of advanced technologies such as AI and 5G.
Agriculture and precision farming: While manufacturing and healthcare were early adopters of digital twin, agriculture is an emerging sector. Digital twins empower farmers with data-driven insights for precision farming. Virtual models of crops and farmland help optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control or can continuously monitor and predict a milch animal’s poor health, equipment malfunction, soil dryness, or temperature change. With a significant portion of the Indian population reliant on agriculture for employment, adopting digital twins in this sector has the potential to modernize traditional farming practices and bolster food security.
A comprehensive table below describes more industry applications and various use cases that are getting implemented.